INSTRUCTORS:
Address
Plot 2632, Princess Road -Kimbejja Namugongo Division, Kira Municipality View mapCategories
PDO TrainingPROGRAM UNIT PDO 206: Financial Management
Session 1: Saving Habits
Session 2: Remittances and Safe Banking
Session 3: Financial Warning and Advice
PROGRAM UNIT PDO 206: Financial Management
| Suggested Total Duration: 4 Hrs. | |
| Suggested Duration | Session |
| 2 Hrs | Session 1: Saving Habits |
| 1 hr | Session 2: Remittances and Safe Banking |
| 1 Hr | Session 3: Financial Warning and Advice |
Module Aims
By the end of the module, participants should be able to:
- Explain how to maintain savings, manage income, and develop a healthy spending habit.
- List different remittance methods and explain how to use them.
- Explain the different financial losses and mistakes as well as beneficial warnings.
- Provide alternative types of bank accounts and documents needed to open them.
Session 1: Saving Habits
Session Objectives
By the end of this session, participants should be able to:
- Understand the salary and its equivalent.
- Have a clear financial plan for their migration journey.
- Have a clear plan of how much to save and how long it will take to achieve the target.
| Suggested Duration | 2 Hrs |
| 30 min Managing your Money
30 min Managing Expenses 30 min Creating a Budget 30 min Dos and Don’ts |
|
| Methodology: Reflections, brainstorming, think-pair-share, discussions, demonstrations, presentations, and guest speakers. | |
| Facilitator Materials: Flip charts, markers, and video clips. | |
| Participants Materials: Copies of the slides or takeaway notes. | |
Session Activities
- Share experiences on how the participants have been managing their incomes while in Uganda.
- Brainstorm on how they anticipate to effectively manage their salaries while in the COD.
- Share experiences on the financial flaws in the management of their finances prior to making the decision to apply for a migrant job.
- Share experiences on how they have raised money that is facilitating their migration costs to the COD.
- Explain how they are going to manage their finances after settling in employment in the COD.
- Draft a budget of expenses vis-à-vis income of the first month in the COD.
KEY SESSION READING MATERIAL
Salaries, Expenses and Savings
Explain the concept of salaries, expenses and saving, and give advice on how to manage spending and saving money in the country of destination and how to remit money to Uganda.
What is a Salary? – Salary is money you receive from your employer as per the contract of employment. This can also include allowance (including transport and accommodation), overtime, bonus, etc. Salary is paid at the agreed terms but usually at the end of the month. In some countries, especially Europe where they pay hourly, some people receive salaries at the end of the week.
What is an Expense? – Expenses are the needs and wants you pay for or buy using your salary.
What is Saving? – It is the money you set aside for safekeeping.
Managing your Money
Paying for the cost of migration
People typically use different options to pay for their migration costs. Some migrants and families may use their saving to pay for all the migration costs. Some migrants and families sell their assets, borrow from moneylenders or banks. Keep in mind that if you borrow the money from the moneylender or bank, these costs will have to be paid in future by your salary. Make sure that you fully understand the cost and the terms of the loan and get these in writing. This is important in case there is a dispute later on.
When deciding how you will pay for migrations cost, keep in mind that:
- You have many options available to pay for migration costs. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages. It is important to learn about and evaluate these different options with your family members.
- You may have to use more than one option to pay for your migration costs. Try to choose the least expensive option whenever possible. Try to avoid high-interest loans and consider formal financial institutions, which may offer lower interest rates than local moneylenders.
- Once you have decided on a financing option, shop around and ask questions to find the best deals and to be informed. Remember that information is power.
Tips on Managing Money
- Have clear short-term and long-term savings goals; successful migration starts with having specific goals. Think about what you will use your savings for: buying land, building a house, capital to start a business, paying for education or other reasons.
- Discuss your short-term and long-term saving goals with your family. Goals are often different between family members as younger and older people are at different stages in their lives. In the family, it is important to acknowledge and respect that each member will have different goals depending on where they are in their life cycle. Remember that saving priorities may change over time; you should regularly revisit and re-evaluate the agreed saving priorities.
- Collect all the information needed to plan well – calculate your expenses.
- Open a bank account. You can open a bank account in your country of destination. This is usually with the help of your sponsor. It is also very advisable to open a bank account in Uganda before you leave. This will help with remitting your money or saving your money. You will be asked to sign a few documents and pay an initial deposit. You will require your national ID or passport to open the account. You can request for an automated teller machine (ATM) card which you can leave with a trusted member of family or keep it for your own access to your money. You are recommended to send money to your family through the bank where you opened the account. Remember to tell your family how much you will be sending home.
Saving Money
For many of you, this will be the first time you receive a big salary. Earning money is a good thing but you also have many choices on how to spend your money. If you spend your money wisely, you will have a better chance of reaching your goals. Be careful, if you spend your money on unnecessary things, you may run out of money.
When abroad, you are far away from home; you will need to be responsible and take care of yourself. Saving money for yourself can help you reach your goal. It can also protect you in case you are sick or if another emergency happens.
Spending Needs and Spending Wants
“Needs” are things that are important to your life.
“Wants” are things that may be nice but sometimes prevent us from reaching our goals.
Note: This does not mean that everything we want is bad; sometimes it is okay to spend money on our wants. However, if you spend too much money on wants, you will run out of money and never reach your goal.
Examples of needs and wants
| Needs | Wants |
| Debt payment
Accommodation Food Utilities Transport Remittances (School fees for children, medical care for parents, upkeep for family) Phone and internet |
Mobile phone
Entertainment Shoes Cosmetics Remittance (birthday, wedding, funeral) |
How to maximize your savings
- Spend on needs, and not wants.
- Save a little money every month.
- Do not buy something new if you already have an old one that works.
- Buy fewer gifts for friends and family when you return to your home. Make sure to talk about this and agree as a family.
- Spend less on parties, festivals, birthdays, weddings, and funerals.
- Carry less money in your pocket; keep your money in a safe place.
- Do not remit your entire savings to your family.
- Look at your long-term goal and think about it every day.
Creating a Budget
A budget is an estimate of your income and how you will spend it in future. A budget can help you manage your money better and decide if you should cut any of your expenses.
Saving Money by Creating a Budget
- To be able to save money, it is important to make a monthly budge for yourself.
- List all your regular expenses for a month (rent, food, etc.) and write down how much they cost; this is the money you have to spend every month.
- You need to calculate how much money you need to send home if you are repaying a loan.
- Keep some money aside for emergencies (in case you fall sick, or a family member gets an accident).
- Set aside money for what you want, though you should not spend too much on wants.
- Deduct all the above from the salary; what is left is your savings.
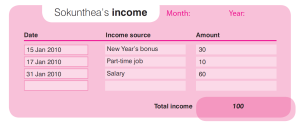
Keep Track of Your Income
This will help you see how much money you are earning per month. You can make your own income statement.
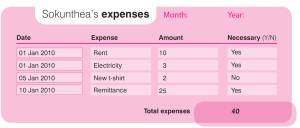
Keep Track of Expenses
This will help you see which expenses you can reduce or cut to help you save more.
How to Control Expenses
- Write down how much you spend on what every month. You should make sure that this amount does not exceed the amount of your budget.
- If you keep spending more than your budget, you should sit down and re-plan your budget.
- Make sure you do not spend more than you earn (that is, you should not borrow money from others except in cases of emergency).
Session 2: Remittances and Safe Banking
Session Objectives
By the end of this session, participants should be able to:
- Know the importance of a bank account and the available bank to open an account at.
- Have the knowledge of the remittance channels in the COD.
- Know the cost of sending remittances.
- Know the advantage of using safe and formal remittance channels.
| Suggested Duration | 1 Hr |
| 20 min Types of Remittance Channels
20 min Advantages of Formal Remittances 20 min Cost of Remittances |
|
| Methodology: Presentations, guest speakers, case study, brainstorming, and discussion. | |
| Facilitator Materials: Flip charts, markers, and flyers from bankers. | |
| Participants Materials: Copies of the slides or takeaway notes. | |
Session Activities
- Experience from former migrant workers in the same field on the funds transfer and types of transfer.
- Brainstorming on the advantages of the money transfer system.
- Deliver a lecture on the cost of remittance / money transfer.
- Guest lecture by officials from banks and money transfer companies.
Remitting Money to Uganda
List and explain the different ways of formal and informal transfer of money overseas to Uganda. Also discuss the cost of sending remittances to Uganda.
Formal transfer system
Formal systems for sending money home include:
- Money transfer companies like Western Union, WorldRemit, UAE Exchange, and Dahabshiil
- Commercial banks
- Forex exchange bureaux
To use money transfer companies like Western Union, you must go to one of their offices/ branches and deposit the money along with the details of the person you are sending it to. In Uganda, that person will go to the nearest office of the transfer company and show their ID proof to get the money.
- You must fill out the money transfer form at the office and submit the form along with the payments (in the form of cash, cheque, etc.) at the counter.
- Make sure the names and other details of the person you are sending the money to match the names and details given on their ID proof.
- You must tell the person that you have sent money through the money transfer company so that they know where to go pick it from.
- The funds will normally be transferred in minutes and the other person will be able to pick up the cash immediately.
Major Money Transfers Companies
Internationally
- Western Union
- MoneyGram
- WorldRemit
- Xpress Money
GCC Money Transfer Companies
- UAE Exchange
- Dahabshiil
- Al Fardan Exchange
Remitting Money through Banks via Electronic Transfer
- You need to have all the details of the bank account of the person you are sending money to (name, address, phone number, bank name, and branch name) as well as the SWIFT code of the bank).
- You can go to a bank in the destination country you are working in or use the bank’s online banking website to send money to an account in the same bank or in another bank.
Sending a Cheque
- Your bank will give you a cheque book which has several cheques you can tear out.
- Each cheque is a slip of paper on which you can write the amount of money you want to give someone along with their names. You can send the cheque to that person, and they go to the bank and deposit it to get paid.
- The cheque can be made “Payable to bearer” which means that whoever has the cheque can go to the bank and collect the money or it can be made payable to a specific person, in which case only that person will be able to deposit the cheque and collect the money.
Advantages of Formal Transfer
- Formal transfers are safe; you can be sure the money reaches the person you want it to, since there is no chance of people cheating you or stealing the money.
Disadvantage of Formal Transfer
- Formal systems require a lot of paperwork (forms to be filled, documents and proof to be submitted, etc.) which can be intimidating if you are not used to them.
- Some formal systems can be slow, taking up to a few days for the transfer. Online or electronic transfers, however, normally take only a few minutes.
- Formal systems can also be more expensive since banks and money transfer companies might charge more than informal transfer agents.
Informal Transfer Systems
This is the type of transfer system that operate outside the regulated banking and financial channels.
- Personal transfer – This is when you entrust money with a person that is traveling to your home country in hope of him/her delivering it to your family.
Cost of Remitting Money
The cost of sending remittances can be divided into two parts:
- There are charges to be paid every time you transfer money (e.g., you have to pay commission when using aan agency like Western Union). This can be a fixed fee or a percentage of the money you are transferring.
- There is the cost in the form of exchange rate. Different options (banks, money transfer companies) will convert your foreign currency to Uganda shilling at different rates when you transfer the money. Exchange rates keep changing; so, before you pick an option for transfer, check to see what exchange rate is being offered. Migrants can utilize the services on the IOM App MigApp for the current exchange rates across the globe. You can also check with your friends on what exchange rates they are getting when sending money home.
Do not try to send money through illegal or unregistered agencies, since they might cheat you and you will lose all the money. Depending on the local laws in the country you are working in, there will be a limit on the transactions you can make in a month.
Exercise
- Filling a bank account opening forms and setting standing orders.
- Filling a funds transfer form.
Session 3: Financial Warning and Advice
Session Objective
By the end of this session, participants should be able to:
- Know the common financial mistakes migrant workers make.
- Understand the changing trends that cause financial losses.
- Know how best to avoid the financial mistakes.
| Suggested Duration | |
| 1 hr. Financial Warning and Advice
|
|
| Methodology: Presentations, guest speakers, brainstorming, case studies, and reflections. | |
| Facilitator Materials: Flip charts, markers, and video clips. | |
| Participants Materials: Copies of the slides or takeaway notes. | |
Session Activities
- Experience sharing from participants on the financial mistakes they have committed.
- Experience sharing from former migrant workers on financial mistakes.
- Brainstorm on the practical strategies to overcome financial mistakes.
Financial Warning and Advice
- Invest in areas or things you are familiar with.
- Invest in areas where you have full control.
- Make sure you have a percentage of saving and percentage of investing.
- Never send all your extra income back to your family members.
- Never get out a loan in order to send a remittance unless it is an emergency.
- Never use informal transfer to send remittances.
- Do not save a lot of money on your foreign account.
- Avoid getting credit cards; if you have been given one, do not activate it.
- Avoid getting excited by bank promotions especially to use the credit card/acquire loans (electronic gadgets, cars).
- Avoid getting international loans if you have no proper and clear payments.
- Avoid malpractices with your accounts, e.g., false withdrawals or false claims.
- Do not gamble; it is addictive and risky.
PDO Training
ENROLL